Diagnosis of Intersection syndrome & Dequervain’ tenosynovitis may pose challenge.
According to Parellada AJ et al distal intersection tenosynovitis of the wrist is a lesser-known extensor tendinopathy. Intersection syndrome is a condition that should be differentiated from DeQuervain's stenosing tenosynovitis, as there are many subtle differences in treatment and prognosis. Hanlon DP et al discussed intersection syndrome, describing its characteristic clinical and anatomic features in journal of emergency medicine. They highlighted differences in the areas of diagnosis and treatment relative to the better known DeQuervain's tenosynovitis.
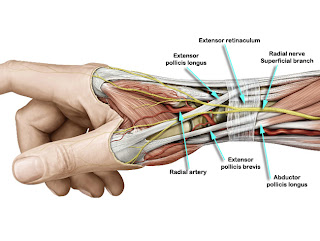
Parellada AJ et al presented the MRI imaging findings of extensor tenosynovitis at the distal intersection or crossover between the second (extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) and brevis (ECRB)) and third (extensor pollicis longus (EPL)) extensor compartment tendons, and the anatomical details that may play a role in the pathogenesis of this condition. They concluded that distal intersection tenosynovitis may be related to the biomechanical pulley effect exerted by Lister's tubercle on the EPL tendon as it leaves the third compartment and crosses over the extensor carpi radialis tendons, as well as the constraining effect of the extensor retinaculum.
Key to diagnosis:
1. Site of pain presentation: intersection site which is proximal and dorsal to dequervain’s site of pain occurance.
2. Cyriax soft tissue tension.
3. Palpation for tenderness.
See the following URL dequervain’s disease:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wiqpJpeYP-E
See the following URL for intersection syndrome:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SyM-HCVHSrM
Parellada AJ et al presented the MRI imaging findings of extensor tenosynovitis at the distal intersection or crossover between the second (extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) and brevis (ECRB)) and third (extensor pollicis longus (EPL)) extensor compartment tendons, and the anatomical details that may play a role in the pathogenesis of this condition. They concluded that distal intersection tenosynovitis may be related to the biomechanical pulley effect exerted by Lister's tubercle on the EPL tendon as it leaves the third compartment and crosses over the extensor carpi radialis tendons, as well as the constraining effect of the extensor retinaculum.
Key to diagnosis:
1. Site of pain presentation: intersection site which is proximal and dorsal to dequervain’s site of pain occurance.
2. Cyriax soft tissue tension.
3. Palpation for tenderness.
See the following URL dequervain’s disease:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wiqpJpeYP-E
See the following URL for intersection syndrome:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SyM-HCVHSrM

Comments
Post a Comment